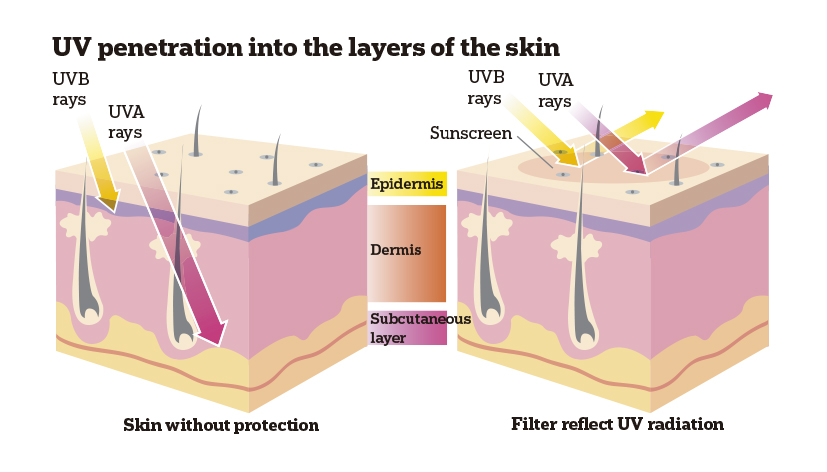
Protection against ultraviolet rays
Thanks to solar radiation, the human body synthesises vitamin D, which is essential in some of the organism’s processes that help to prevent osteoporosis and rickets, for example. Therefore, the sun does not only cause damage. The key is to find a balance and act with caution: avoid the hours of maximum radiation, protect against the ultraviolet rays and moisturise the skin.
The sun provides heat, energy and brings many benefits for health, amongst which the healing of wounds, its role in the prevention of osteoporosis or acne stands out; it even helps reduce cholesterol and blood pressure. The problem arises when there is a constant, indiscriminate exposure. Ultraviolet radiation, UVB, plays an important role in the development of skin cancer and in premature ageing. Excessive exposure also causes dryness or burns. Studies corroborate that between 70% and 90% of basal cell carcinomas are developed in areas of the head and neck exposed to sunlight. Therefore, dermatologists recommend a progressive exposure to sun rays, slowly increasing.
Now that summer is on the way, it should be taken into account that a large part of the population has not received any solar radiation directly for some time; therefore to prevent burns, care must be taken with exposure to the sun. The experts recommend the use of sunscreens and other protection elements, such as specific clothing or hats and/or caps. Sunscreen must be applied before going out into the sun and it must be reapplied generously every two hours. To choose the right sunscreen, there are several factors to be considered. On the one hand, skin colour. For example, light skins are more sensitive to exposure to the sun than darker ones. The season must also be taken into account, as well as how long is the skin going to be exposed and whether there are any previous skin problems. There is a great deal of educational work and campaigns to be done regarding the pairing formed by sun and skin problems. In spite of the fact that 92% of people acknowledge that exposure to the sun can generate health problems, only 18% of them always protect their skin. Dermatologists recall that it is essential to establish suitable habits against sun radiation to be able to take advantage of its benefits and to minimise its risks.
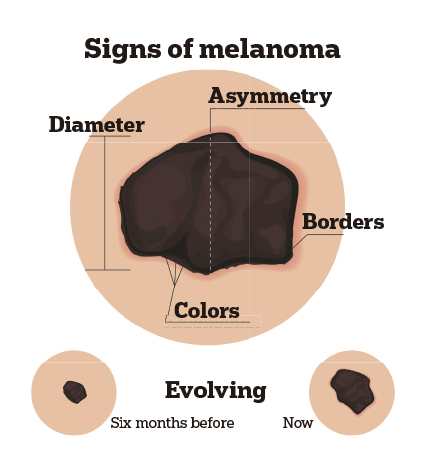
Early diagnosis, vital in skin cancer
The most frequent skin problems are viral infections, eczema, psoriasis, acne, fungal infections, hives, alopecia or moles. But, currently, a very important part of dermatology is comprised of skin cancer, with a large increase in cases in recent years, which are closely related to exposure to the sun. 90% of these appear on the areas of the skin exposed to the sun: the face, neck, ears, hands and forearms. Early diagnosis is one of the most effective weapons in the fight against this disease. This early detection increases the possibilities of successful treatment exponentially which, in initial phases means a better prognosis in the evolution of the cancer.
The two most common types of cancer, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, have high probabilities for being cured. Melanoma, the third type, is more dangerous and usually has a worse prognosis. According to the Observatory of the Spanish Association Against Cancer (AECC in its Spanish initials), in Spain around 5,500 cases of melanoma are diagnosed every year. The patient’s prognosis will depend, to a large extent, on the stage of the tumour and whether the cancer cells have reached organs near the skin melanoma. However, an increasing amount of research is revealing other factors that affect patient survival. One of these studies, focused on melanoma, was presented at the 1st AEDV Virtual Congress Autumn 2020, last November. Amongst other conclusions, it was observed that being over the age of 70 years means an increase in mortality due to melanoma.
Which simple steps can be taken to protect against the sun?
1.- Avoid exposure to the sun in the central hours of the day. The UV sun rays are stronger between 10 am and 4 pm.
2.- Take the UV index into account. This data helps plan open air activities to prevent excessive exposure.
3.- Take advantage of the shade, without forgetting that trees, sunshades or awnings do not give complete protection against solar radiation.
4.- Use protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats or sun glasses with a 99-100% protection rate. Loose clothing with tightly-woven fabric also protects against the sun.
5.- Apply sunscreens with solar filters. Spread the cream generously over the exposed skin and repeat the application every two hours.
6.- Protect children, since they are usually more vulnerable to environmental risks. Babies must always be kept in the shade.