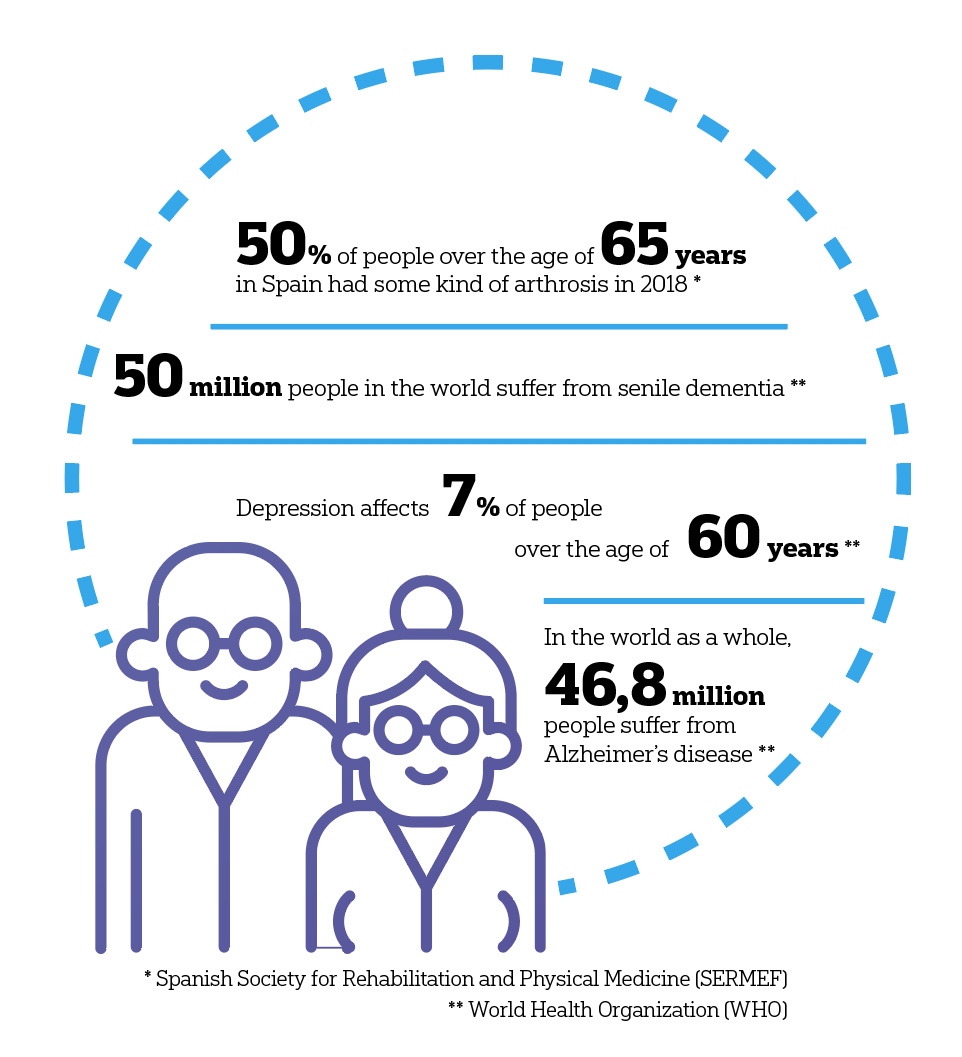
Geriatric diseases that occur from the age of 65 onwards
The WHO indicates that in 2050 there will be more older people than young people and that the elderly population will have doubled, reaching 2,100 million.
Life expectancy has increased a great deal in recent decades. Today, most of the population has a life expectancy of over 60 years; in Spain, this figure is already around 80 years. In fact, Spain is one of the European countries with the oldest population. This increase in older people sets forth challenges in the health area. According to the WHO, in 2030 one in every six people will be over 60 years of age. That is to say, from now to 2030, the percentage of the planet’s inhabitants of over the age of 60 will increase by 34%. And it will continue to rise. This will mean that in 2050, the world elderly population will have doubled, reaching 2,100 million. In fact, the number of citizens over the age of 60 will be greater than the number of young people and teenagers. That is to say, with a population that is older than ever before, it is normal for doctors’ surgeries to be full of adults suffering from some kind of ailment every day. Many of these illnesses are chronic and most of them are very common in the senior population. Therefore, in the health field this means many challenges. Amongst others, how to attend to the increase in demand for medical care and to plan this care in the long term.
In spite of the fact that today, we are reaching old age in much better conditions that previously, the body gradually becomes weaker and its ageing is unavoidable. Therefore, certain pathologies cannot be fought against and these get worse as the years go by. The most common geriatric diseases are related to blood circulation, bones and neurodegenerative problems. They are common, but thanks to technological innovation and research, nowadays they can be tackled in a much more effective way.
Diseases that are most common in the elderly
ARTHRITIS
What it is: It is an inflammation in the joints that causes pain when making certain movements. It is important to treat it to prevent it from turning into arthrosis. Age or family history are risk factors for suffering from this disease.
Treatment: This rheumatic pathology is very common and it can be treated with rehabilitation and using anti-inflammatory medicines.
ARTHROSIS
What it is: It is the degeneration of the joint cartilage (wear and tear of the joints) and it has a very high incidence in old age. It makes moving difficult and causes pain when the affected joint is moved.
Treatment: Medicines are prescribed to relieve the pain and in the most serious cases, surgery is used to replace the damaged joints with prostheses.
OSTEOPOROSIS
What it is: It is a degenerative disease that consists of a decrease in bone density. Therefore, the bones become weaker. This can cause falls and accidents that derive in bone fractures and breakages. Hip fractures are one of the most common breakages in the elderly.
Treatment: Drugs are used to prevent the loss of bone mass and a healthy diet is advised, with an extra amount of calcium and vitamin D, in addition to doing sport regularly.
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
What it is: The ageing of the brain causes the nerve cells to atrophy in some areas, causing serious damage. The patient suffers from a cognitive deterioration that involves a progressive loss of memory and of mental skills.
Treatment: This neurodegenerative disease has no definitive cure, although there are some therapies that slow it down or delay its symptoms, such as music therapy or cognitive stimulation. There are also pharmacological treatments to help ease its effects.
PARKINSON’S DISEASE
What it is: It is a neurodegenerative disease that causes the death of brain cells. Today, the causes behind it are still not exactly known. The symptoms include shaking limbs, rigidity in the body or lack of coordination.
Treatment: In the first instance, medicines that compensate the loss of brain dopamine are recommended. The disease cannot be cured permanently, but the symptoms can be controlled.
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
What it is: It is a cardiovascular pathology where the force exercised by the blood against the blood vessels is too high. Suffering from this ailment increases the risk of strokes, chest angina, heart attacks or cardiac insufficiency. Additionally, blood pressure increases with age; therefore it is a common pathology in patients from the age of 65 years onwards.
Treatment: Healthy habits are recommended for inclusion in daily life, such as walking every day, maintaining a correct weight and moderating salt and alcohol intake.
DEPRESSION
What it is: This mood disorder is becoming more common amongst the elderly. Loneliness, fear of falling ill, the death of friends… make sadness turn into depression, a mental disease that also increases the cases of insomnia and memory loss.
Treatment: The treatment counteracts the emotional and physical consequences. Psychological therapy and family accompaniment improve mental health, alongside pharmacological treatment.
SENILE DEMENTIA
What it is: This disease involves a deterioration of the cognitive function; that is to say, of the capacity to process thought. For this reason, it affects memory, thoughts, reckoning, language and understanding. It causes disorientation, confusion or memory loss.
Treatment: The most common options are pharmacological treatments and occupational therapy. Additionally, the incorporation of healthy habits and setting a routine and timetable also minimise the symptoms of senile dementia.